
The mathematics of piano tuning
3. The equal-tempered keyboard
The interval from a note to the note of twice the frequency is called
an octave, while
the interval to the note of 3/2 the frequency
is called a perfect fifth. These are the most natural intervals
in music. But for a piano to be able to play down an octave and up
perfect fifth for each of its notes would require an infinite
number of keys. The compromise solution
in common use since the middle of the nineteenth century
is equal temperament. It is based on a rational
approximation to log23. The continued fraction
approximation of frac(log23) yields 1/2, 3/5, 7/12, 24/41, ...
as best rational approximations. The one to take is 7/12.
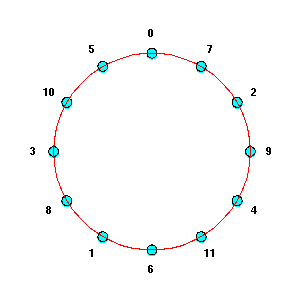 |
With 7/12 as approximation to frac(log23), iterating the
"third harmonic" construction yields exactly twelve pitch classes.
If "0" corresponded to C on a piano, then the pitch classes would run
as follows:
| 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 |
| C | G | D | A | E | B | F# | C# | G# | D# | A# | F |
Since the interval from each note to the next is a (not quite perfect) fifth,
this sequence of
pitch classes is referred to as "the circle of fifths."
|
The beauty of
equal tempering is that the whole arrangement has a rotational symmetry
of order 12. A piano piece written with starting pitch C can be "transposed" up
so as to start with F by shifting each note five steps clockwise. No new
notes are required. All the
relationships between the notes of the piece will be the same: it will
be the same piece of music, just set higher.
The price paid for this convenience is that none of the intervals,
except the octaves, sounds quite right.
In the New
Grove Dictionary of Music and Musicians there is a 14-page entry
for "Temperament" which explains the history of the problem and the
pros and cons of the various solutions. In particular it is still
not known for sure whether the "well-tempering" consecrated by Bach was equal
tempering or not. See also the Grove entry for "Well-tempered clavier."
Jim Loy's web-page The Well-Tempered Scale comes down squarely on the "or not" side.
Comments: webmaster@ams.org
© copyright 2000, American Mathematical Society.

