p p p p = phosphate
.. \ / \ / \ / \ / ...
s s s s s = sugar
| | | |
b b b b b = base
where each b can be any one of four bases:
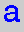 = adenine,
= adenine,
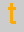 = thymine,
= thymine,
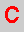 = cytosine,
= cytosine,
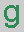 = guanine.
= guanine.
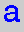 ,
,
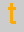 ,
,
 ,
,
 when the strand is being read from the 3'-end to the 5'-end,
and
when the strand is being read from the 3'-end to the 5'-end,
and
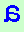 ,
,
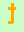 ,
,
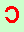 ,
,
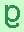 when the strand is being read the opposite way, that is, from the
5'-end to the 3'-end.
when the strand is being read the opposite way, that is, from the
5'-end to the 3'-end.
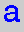 on one strand is a
on one strand is a 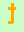 on the other,
and opposite every
on the other,
and opposite every 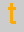 is an
is an 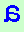 . Likewise opposite every
. Likewise opposite every
 on one strand is a
on one strand is a 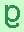 on the other,
and opposite every
on the other,
and opposite every  is a
is a  . A typical stretch
of the DNA molecule looks like:
. A typical stretch
of the DNA molecule looks like: