MAT 331 Homework Exercises. Week 5 (Oct 19, 99).
NOTE: [No Maple] means that the problem does not involve
Maple, except as a word processor to write your solution. In this case
you can alternatively turn in a short paper, if you are more
comfortable with that.
- #17 (exp. 10/26)
- [No Maple] Recall that for a differentiable function
of two variables, f, the level curve corresponding to the constant
c is defined as the set of all points (x, y) for which f (x, y) = c.
Prove that the gradient of f is always orthogonal to the level
curve. That is, in each point (x, y) of the level curve corresponding
to c,
 f (x, y) is orthogonal to the tangent vector to the
curve in (x, y).
f (x, y) is orthogonal to the tangent vector to the
curve in (x, y).
- #18 (exp. 10/26)
- Find all the critical points of
g(x, y) = (2x2 - x)(y2 - 1) and determine which ones are local maximum, minimum
or saddle points. What are the absolute maximum and minimum of
g? [Hint: You may find array, matrix and other
commands form the linalg library useful.]
- #19 (exp. 10/26)
- Define a Maple function h(x, y) that is 0 in
the first quadrant, y sin x in the third quadrant and xy in the
rest of the plane.
- #20 (exp. 11/2)
- Write a Maple procedure that takes as input two
integers a, b, and returns the following objects: l, s,
p. Here l is the list of all primes between a + 1 and b(extremes included), s their sum, and p their product.
Also, have Maple print on the screen ``Above average'' if the
number of these primes is greater than
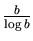 -
- 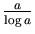 ; ``Below average'' otherwise. [Hint: See
isprime, print. Check op on how to add an element to
a list]
; ``Below average'' otherwise. [Hint: See
isprime, print. Check op on how to add an element to
a list]
Translated from LaTeX by MAT 331
1999-10-19